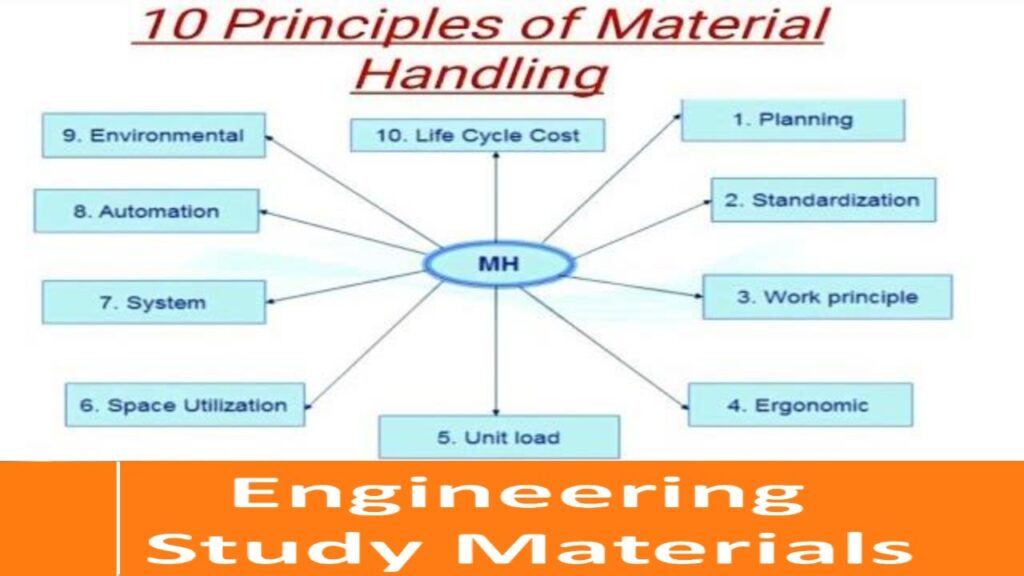
The Principles of Material Handling: Ensuring Efficiency with Handling Equipment
Material handling is a critical aspect of any industrial operation. It involves the movement, storage, and control of materials within a facility or between different locations. Efficient material handling processes are essential for optimizing productivity, reducing costs, and ensuring the safety of workers.
In a YouTube video titled “Principles of Material Handling | TEN(10) Principles | ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIALS,” the fundamental principles of material handling are explored in depth. This article aims to provide an insightful analysis of these principles, their importance, and how handling equipment plays a crucial role in their implementation.
Principle 1: Planning
Effective planning is the foundation of successful material handling. It involves considering factors such as facility layout, space utilization, equipment selection, and workflow optimization. By carefully planning material handling activities, companies can streamline their operations, minimize bottlenecks, and maximize efficiency.
Principle 2: Standardization
Standardization refers to establishing uniform procedures and practices for material handling operations. This principle simplifies training, enhances productivity, reduces errors, and promotes safe working conditions. Handling equipment that adheres to established standards facilitates seamless integration with the overall material handling process.
Principle 3: Work
Optimizing the workload is crucial for efficient material handling. This principle emphasizes careful organization and scheduling to ensure that each task is assigned to the most suitable equipment and personnel. By matching the workload to the available resources, companies can minimize downtime, eliminate unnecessary steps, and improve overall productivity.
Principle 4: Ergonomics
Considering ergonomic factors is vital for the health and safety of workers involved in material handling. Ergonomically designed handling equipment reduces physical strain, minimizes the risk of musculoskeletal disorders, and enhances employee well-being. Investments in ergonomic solutions not only promote worker safety but also contribute to long-term productivity gains.
Principle 5: Unit Load
The unit load principle focuses on consolidating smaller items into larger loads for more efficient handling. This reduces the number of trips required, optimizes storage space, and reduces the chances of damage during transportation. Handling equipment such as forklifts, conveyors, and stackers play a pivotal role in facilitating the unit load principle.
Principle 6: Space Utilization
Effectively utilizing available space is essential to maximize storage capacity and minimize wasted areas. Material handling equipment should be designed to optimize vertical and horizontal space utilization within facilities. Automated systems, such as robotic palletizers, can efficiently stack and organize materials, ensuring no space is left unused.
Principle 7: System Integration
System integration involves harmonizing all material handling activities within a facility. From order picking to inventory management, the seamless integration of various processes eliminates bottlenecks, reduces errors, and enhances overall efficiency. Advanced handling equipment integrated with warehouse management systems ensures smooth operation and accurate data tracking.
Principle 8: Automation
Automation has revolutionized material handling by enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Automated handling equipment, such as AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) and AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems), can streamline processes, minimize human error, and improve productivity. The implementation of automation should be carefully planned to ensure compatibility with existing operations.
Principle 9: Environmental Considerations
In today’s age, environmental sustainability is a key consideration for businesses. Material handling equipment should be designed to minimize energy consumption, reduce waste generation, and promote eco-friendly practices. Implementing green solutions not only benefits the environment but also enhances the reputation of the company.
Principle 10: Life Cycle Cost
The life cycle cost principle emphasizes the evaluation of handling equipment beyond its initial purchase price. Factors such as maintenance, repair, and energy costs over the equipment’s entire life cycle should be taken into account. By considering long-term costs, companies can make informed decisions regarding their handling equipment investments, ensuring maximum value for their money.
In conclusion, the principles of material handling highlighted in the YouTube video provide valuable insights into optimizing efficiency and safety within industrial operations. Implementing these principles requires the effective use of handling equipment, which plays a pivotal role in facilitating seamless material flow, reducing errors, and improving productivity. By adhering to these principles and harnessing the power of modern handling equipment, industries can achieve their operational goals while ensuring a safe and productive working environment for their employees.
Article by [Your Name]
Handling Machine
“Essential Principles for Efficient Material Handling: A Comprehensive Guide on Engineering Study Materials and Handling Equipment”